What is Metal Extrusion?
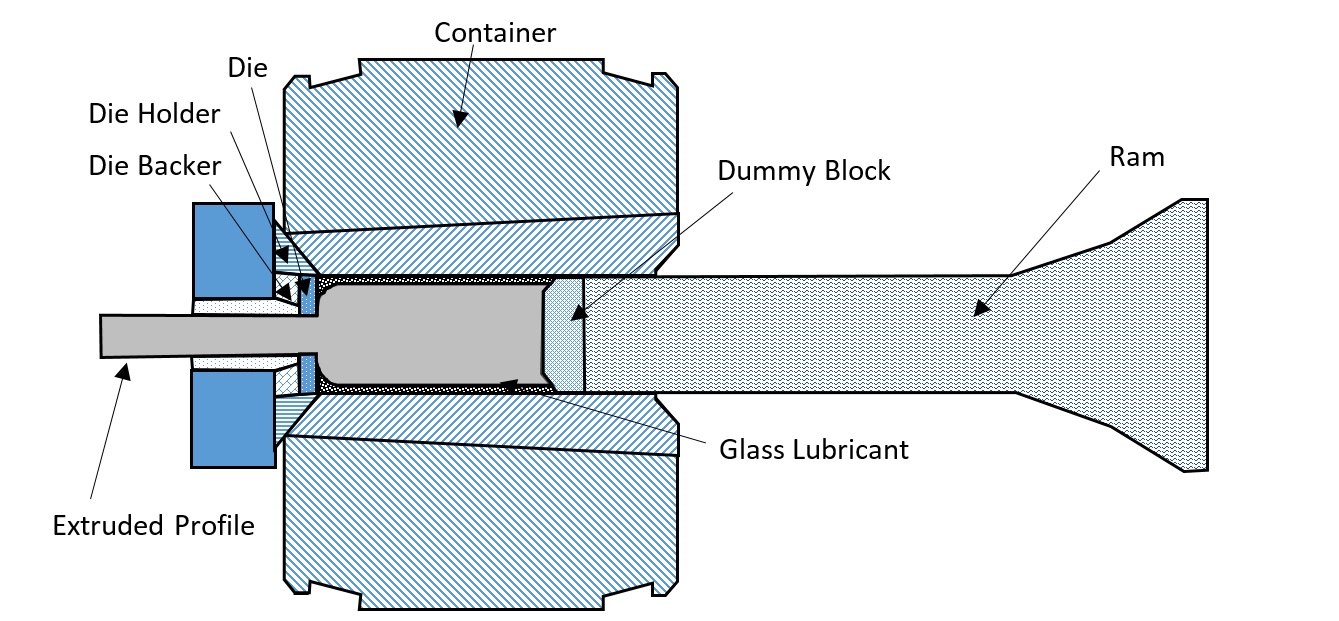
Metal extrusion is a process used to create longer objects with a fixed profile by pushing a cylindrical billet inside a closed cavity. The end product is called an extrudate and can have several desired characteristics and qualities. The metal extrusion process was patented by Joseph Bramah and is regularly used to create parts from Steel, Aluminum, Copper, Magnesium, and Lead.
Types of Metal Extrusion Processes
Various types of metal extrusion processes are used today, each with its own set of qualities:
- Direct Extrusion is the simplest and most common type. In this process, the billet is pushed through a press cavity container.
- Indirect Extrusion is the opposite. Instead of the billet, in this case, a hydraulic ram pushes against the billet.
- Hydrostatic Extrusion uses hydraulic fluid to push the billet through the die.
- Lateral Extrusion is mostly when the materials are melted. The die in this process is positioned on the side.
- Impact Extrusion uses a punch to create an extrudate and is mostly used on softer metals.
Characteristics of the Metal Extrusion Process
The metal extrusion process is widely used today, thanks to a fast and high production rate, and low cost. Furthermore, both hot and cold metal extrusion processes can be used. However, hot metal extrusion is easier due to smaller forces needed to create an extrudate.
Characteristics and Qualities of Extrudates
Parts created with the metal extrusion process posses many necessary qualities that make them unique when compared to other methods:
- Pieces created with the metal extrusion process can have a very complex cross-section that stays fixed through the entire length of the part.
- Parts with very thin walls can be produced (down to 1 mm for aluminum and 3 mm for steel).
- The material used in the metal extrusion process is only subjected to compressive and shear stresses. Thanks to that, the method can be used to create extrudates from very brittle materials.
- The processed parts have an excellent surface finish, unlike similar metal forming processes.
- Beneficial elongated grain structure in the processed parts.

 Tech Steel & Materials
Tech Steel & Materials